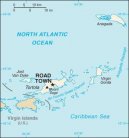
British Virgin IslandsBritish Virgin Islands: Travel tips, articles, photos, gallery, cities database, population, pics, flags, statistics, free maps onlineBack to Countries, Click to read the whole article: British Virgin Islands
Source: CIA >>> |
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
Map of country British Virgin Islands on-line : All cities of country British Virgin Islands : Biggest cities of country British Virgin Islands : Photo to article British Virgin Islands : |
Free IQ test online
An Intelligence Quotient or IQ is a score derived from one of several different standardized tests attempting to measure intelligence. Although the term "IQ" is still in common use, the scoring of modern IQ tests such as the Wechsler Adult Intelligence Scale is now based on a projection of the subject's measured rank on the Gaussian bell curve with a center value (average IQ) of 100, and a standard deviation of 15, although different tests may have different standard deviations. The average IQ scores for many populations have been rising at an average rate of three points per decade since the early 20th century with most of the increase in the lower half of the IQ range: a phenomenon called the Flynn effect. It is disputed whether these changes in scores reflect real changes in intellectual abilities, or merely methodological problems with past or present testing. (Wikipedie)
IQ test lasts approximately 30 minutes and contains 40 questions !
In the IQ test you must focus on the maximum. Test questions are simple. In the IQ test may not use the calculator and paper.
Free IQ test online :
Banner on your page · Visitor's book · Besplatnye igry onlajn · Free games online · CZ Hry · RoboStav
Copyright (c) 2026 by TiptopGlobe.com. All Rights Reserved!
|
Add photo... |
Games Online